Understanding the Impact of Socioeconomic Factors on Health Outcomes
PH
Introduction to Socioeconomic Factors and Health
Socioeconomic factors play a crucial role in determining health outcomes. These factors, which include income, education, employment, and social support, can influence the health of individuals and communities in significant ways. Understanding how these elements interact is essential for addressing disparities in health and promoting equitable health care access.
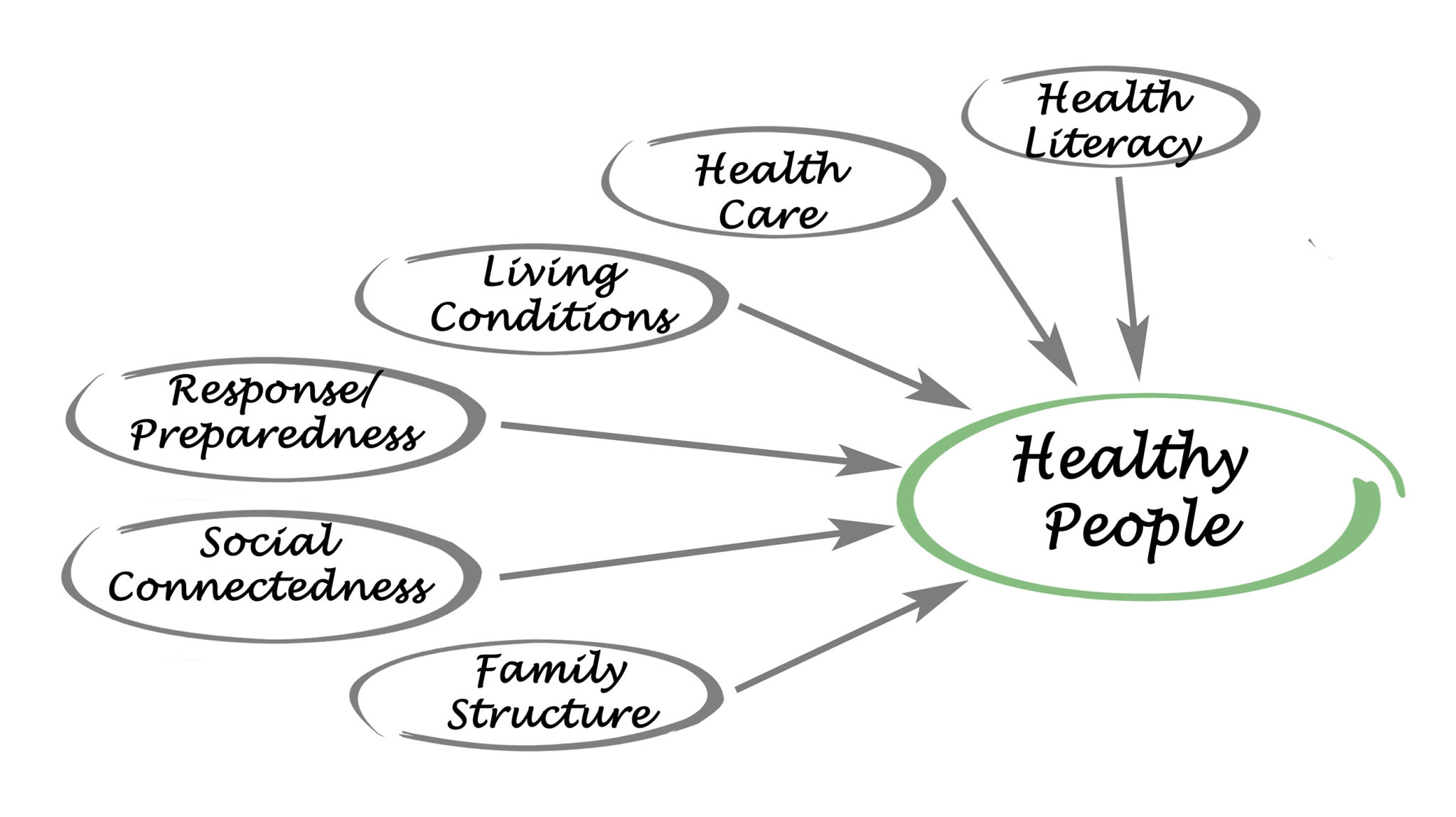
The Role of Income in Health
Income is a fundamental socioeconomic factor affecting health outcomes. Individuals with higher incomes typically have better access to healthcare services, healthier food options, and safe living environments. Conversely, those with lower incomes often face barriers to accessing quality healthcare and may experience higher levels of stress due to financial instability. This can lead to chronic health conditions and shorter life expectancy.
Income inequality can exacerbate health disparities. In communities where the gap between the wealthy and the poor is wide, those at the lower end of the income spectrum often face significant health disadvantages. Addressing income inequality is crucial for improving health outcomes across all populations.
Education as a Determinant of Health
Education is another pivotal factor influencing health. Higher levels of education are associated with better health outcomes, as educated individuals are more likely to be informed about healthy behaviors and have the skills needed to navigate the healthcare system. Education also opens up opportunities for better employment, leading to improved economic stability and health.

The impact of education on health extends beyond individual behaviors. Communities with higher education levels often advocate more effectively for public health resources and policies that promote well-being. This collective action can lead to healthier environments and improved community health outcomes.
Employment and Its Health Implications
Employment status and job conditions significantly affect health outcomes. Having a stable job provides not only financial resources but also social connections and a sense of purpose, all of which contribute to mental and physical well-being. However, job insecurity, unemployment, or poor working conditions can lead to stress and adverse health effects.
Occupational hazards, such as exposure to toxic substances or unsafe work environments, can directly impact physical health. Moreover, jobs that offer inadequate benefits or lack flexibility can make it challenging for individuals to prioritize their health needs.

The Importance of Social Support
Social support networks are essential for promoting positive health outcomes. Strong relationships with family, friends, and community members provide emotional support, increase opportunities for shared resources, and improve mental health. Individuals with robust social networks often experience lower levels of stress and better coping mechanisms during challenging times.
Conversely, social isolation can have detrimental effects on health, increasing the risk of mental health issues and chronic conditions. Encouraging community cohesion and building supportive networks are vital strategies for enhancing public health.
Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities in Health
Efforts to improve health outcomes must consider the broader socioeconomic context. Policies aimed at reducing poverty, increasing educational opportunities, and ensuring access to healthcare are essential for addressing the root causes of health disparities. Collaborative approaches involving government agencies, healthcare providers, community organizations, and individuals are necessary to create sustainable change.
By understanding and addressing the impact of socioeconomic factors on health, we can work towards a future where everyone has the opportunity to lead a healthy life, regardless of their socioeconomic status.